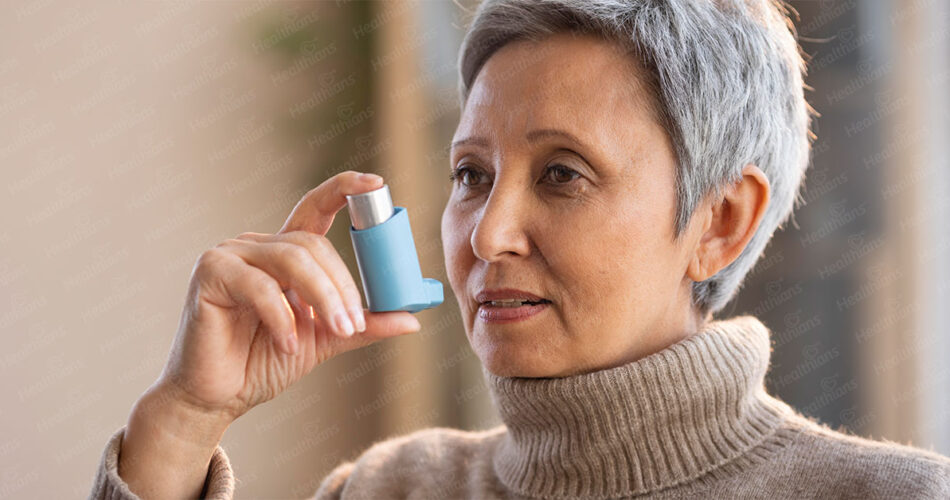
Bronchodilators are a type of medication used to treat respiratory conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and bronchitis. They work by relaxing the muscles in the airways, allowing for easier breathing and increased airflow. In this article, we will discuss the different types of bronchodilators, their mechanisms of action, and their uses.

*Types of Bronchodilators*
There are two main types of bronchodilators: beta-2 agonists and anticholinergics.
1. *Beta-2 Agonists*
Beta-2 agonists, also known as bronchodilators, are the most commonly used type of bronchodilator. They work by stimulating the beta-2 receptors in the airway muscles, causing them to relax and allowing for increased airflow. Examples of beta-2 agonists include:
- Albuterol (Ventolin)
- Levalbuterol (Xopenex)
- Metaproterenol (Alupent)
- Pirbuterol (Maxair)
- Terbutaline (Brethaire)
Anticholinergics
Anticholinergics, also known as antimuscarinics, work by blocking the action of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that stimulates the airway muscles to contract. Examples of anticholinergics include:
- Ipratropium (Atrovent)
- Tiotropium (Spiriva)
- Glycopyrrolate (Robinul)
*Mechanisms of Action*
Bronchodilators work by relaxing the muscles in the airways, allowing for increased airflow and easier breathing. They do this by:
- Relaxing the airway muscles: Bronchodilators cause the airway muscles to relax, allowing for increased airflow and easier breathing.
- Reducing inflammation: Some bronchodilators, such as corticosteroids, can reduce inflammation in the airways, which can help to improve breathing.
- Increasing mucus clearance: Bronchodilators can help to increase mucus clearance, which can help to improve breathing and reduce the risk of respiratory infections.
*Uses*
Bronchodilators are used to treat a variety of respiratory conditions, including:
- Asthma: Bronchodilators are commonly used to treat asthma, a chronic respiratory condition characterised by inflammation and constriction of the airways.
- COPD: Bronchodilators are used to treat COPD, a progressive respiratory condition characterised by damage to the lungs and airways.
- Bronchitis: Bronchodilators are used to treat bronchitis, a respiratory condition characterised by inflammation of the airways.
- Emphysema: Bronchodilators are used to treat emphysema, a respiratory condition characterised by damage to the lungs and airways.
*Side Effects*
Bronchodilators can cause a variety of side effects, including:
- Coughing: Bronchodilators can cause coughing, especially when first starting treatment.
- Throat irritation: Bronchodilators can cause throat irritation, especially when using an inhaler.
- Headaches: Bronchodilators can cause headaches, especially when first starting treatment.
- Nervousness: Bronchodilators can cause nervousness, especially when first starting treatment.
- Insomnia: Bronchodilators can cause insomnia, especially when taking them at night.
*Contraindications*
Bronchodilators are contraindicated in certain individuals, including:
- Pregnant women: Bronchodilators should be used with caution in pregnant women, as they can affect the unborn baby.
- Breastfeeding women: Bronchodilators should be used with caution in breastfeeding women, as they can affect the baby.
- Individuals with certain medical conditions: Bronchodilators should be used with caution in individuals with certain medical conditions, such as high blood pressure, heart disease, and thyroid disease.
*Conclusion*
Bronchodilators are a type of medication used to treat respiratory conditions such as asthma, COPD, and bronchitis. They work by relaxing the muscles in the airways, allowing for increased airflow and easier breathing. While bronchodilators can be effective in treating respiratory conditions, they can also cause side effects and interact with other medications. It is essential to use bronchodilators as directed by a healthcare provider and to report any side effects or concerns.

Other stories
Inhaled Corticosteroids: A Comprehensive Guide
Long-acting Beta Agonists (LABAs): A Comprehensive Guide
Watch Agyemang Rawlings and President Akuffo-Addo dance during the 100th anniversary of Prempeh I.
The job I did for Lord Kenya was not appreciated— Okraku Mantey
View the remnants of GH200 notes that were burnt during the fire.